206. Reverse Linked List

Overview
Just to the topic, we need to revere the input linked list.
Solution 1: iteration
Algorithm
-
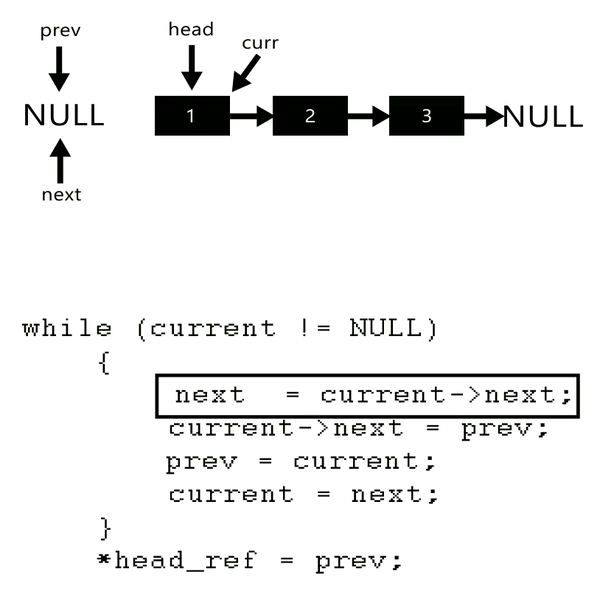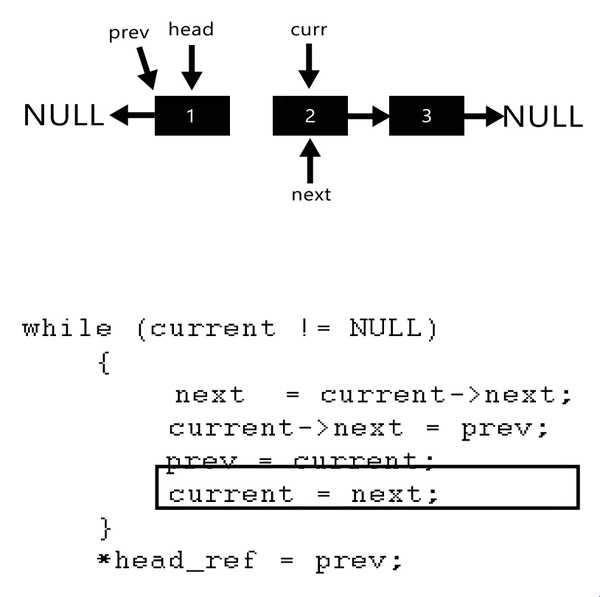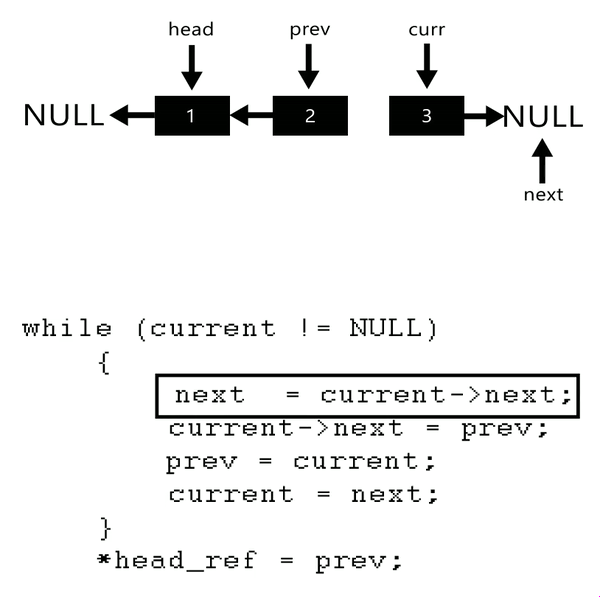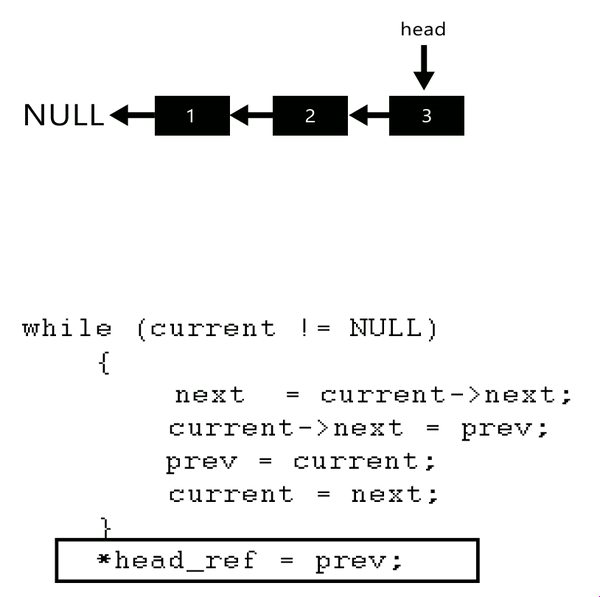
initialize
currenttoheadandprevioustoNone -
Iterate through the linked list:
- Set
nexttocurrent.next.
We need to savecurrent.nextfor removing pointers. - Set
current.nexttopreviousto reverse the link. - Set
previoustocurrentto move pointer for the next loop. - Set
currenttonextto move pointer for the next loop.
- Set
Implement
class Solution: def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: current = head previous = None while current: next = current.next current.next = previous previous, current = current, next return previous
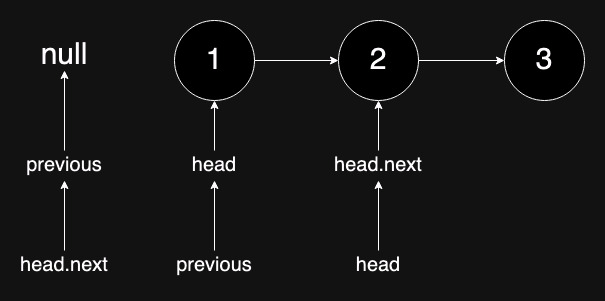
Actually, we don't need current and next can also achieve the pointers moving.
class Solution: def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: previous = None while head: head.next, previous, head = previous, head, head.next return previous
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity: O(n)
Iterating through the linked list takes O(n).
Space complexity: O(1)
Addition variables are constraint that won't grow up with the input, taking O(1).
Solution 2: recursive
Algorithm
-
If
headis None, it shows that recursive has ended, returningprevious. -
Set
nexttohead.next.
We need to savehead.nextto pass it as recursive head. -
Set
head.nexttopreviousto reverse the link. -
Recursively call
nextasheadandheadasprevious.
Implement
class Solution: def reverseList( self, head: Optional[ListNode], previous=None, ) -> Optional[ListNode]: if not head: return previous next = head.next head.next = previous return self.reverseList(next, head)
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity: O(n)
The recursive function will traverse each node, taking O(n) time.
Space complexity: O(n)
The recursive stack needs to store each node and recursively call the next node.
Since we don't employ any optimization techniques, the space complexity is O(n).